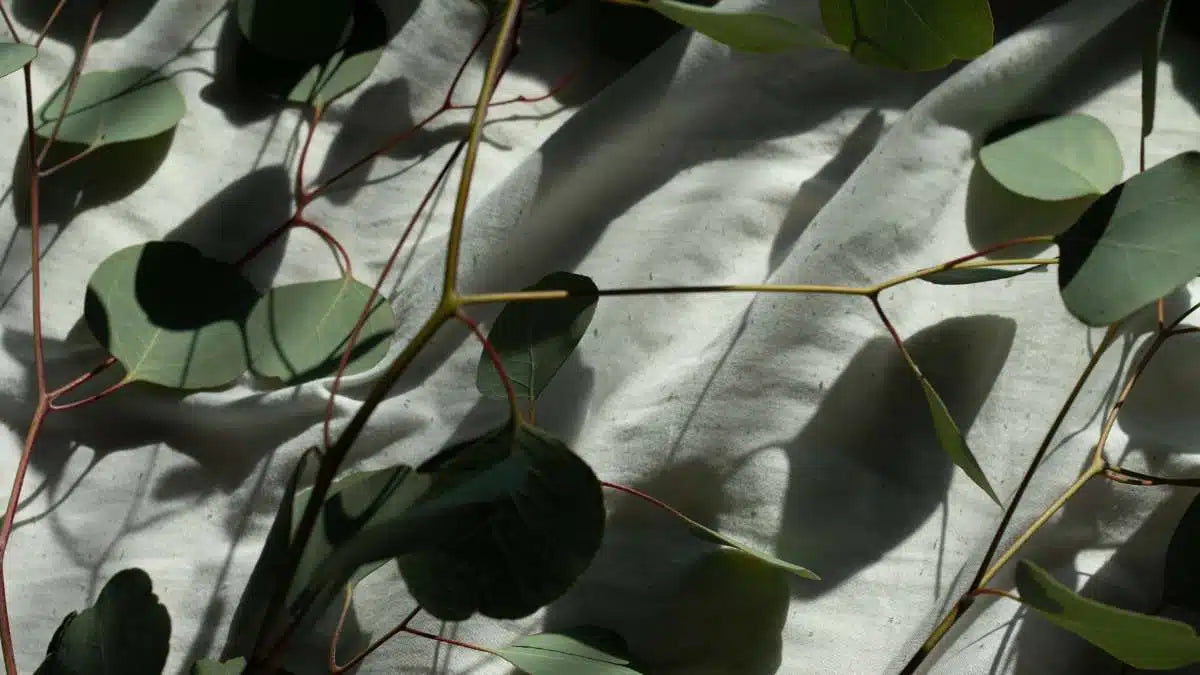
All About Eucalyptus & The Impacts of Tencel
The environmental impact of Tencel is mitigated mostly from the way it is sourced, produced & worn, along with its end-of-life biodegradability, integrating the fabric back into the Earth and the biological cycles of nature.
- Made from the wood-pulp of sustainably managed forests, the fabric is derived from a renewable and regenerative source, meaning the raw material will continue to regrow.
- The manufacturing itself is circular and a closed-loop, with water continuously recycled and 99.8% of solvents used re-integrated into the bio-refineries.
- As a fabric, it is naturally breathable and anti-microbial, meaning it requires less washing. This saves water and preserves garment quality, in turn enhancing its durability and longevity — two key concepts of circular design.
- Finally, as a cellulose-based fibre it is naturally biodegradable, able to return to Earth and help regenerate the forests it was originally sourced from.
It would a good point to mention that circularity systems can be separated into both technical and biological cycles.
In the technical cycle, products and materials are kept in circulation through processes such as reuse, repair, remanufacture and recycling, while in the biological cycle, the nutrients from biodegradable materials are returned to the Earth to regenerate nature.
So, while Tencel is technically sourced from virgin or raw material, its renewable and regenerative nature creates a continuous flow of material and makes it one of the most sustainable fabrics available.




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.